How to measure stock price volatility
Volatility (finance) - Wikipedia
These stocks have strong dividend payout ratios and low debt-to-market-capitalization ratios. The value received from these dividends is more than offset by the depreciation in value of the stocks.
One way to inoculate our portfolios from the problems in Europe is with U. This module of TheStreet University will cover the four main types of volatility measures: Historical Volatility Volatility in its most basic form represents daily changes in stock prices. We call this historical volatility or historic volatility and it is the starting point for understanding volatility in the greater sense.
Historic volatility is the standard deviation of the change in price of a stock or other financial instrument relative to its historic price over a period of time. That sounds quite eloquent but for the average investor who does not command an intimate knowledge of statistics, the definition is most overwhelming. Think of a Pendulum To help you visualize the concept of volatility, think of a pendulum like in the picture below.
The pendulum is constructed from a steel ball, attached to a rope and then suspended from a ceiling. The pendulum starts at the resting state when our ball is at point 2 the mean.
How to Calculate Stock Price Volatility | jyfyyuxy.web.fc2.com
If you raise the ball to point 1 and let it go, the ball would then swing from point 1 to point 3. Over time that ball will swing back and forth always passing though point 2.
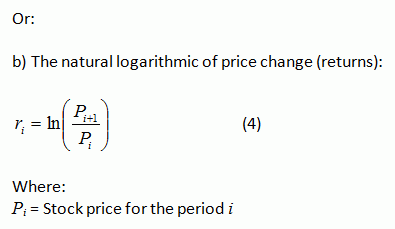
If this were a stock, the difference in distance from point 1 to point 2 or from point 2 to point 3 represents the volatility in the movement of the stock price. So as not to get into any trouble with physicists out there, the formulas for standard deviation and movement of a pendulum are different and I am not equating the two from a statistical perspective. Rather, I am only using the pendulum as a visual aide. Stocks with a swing that is greater from point 1 to point 2 vs.
Now imagine a wind hitting the metal ball. The force of that wind will increase a stock's volatility. Market corrections, increases in uncertainty or other causal factors of risk will be the wind that shifts volatility higher.
Say that there is no wind, but rather calm over the markets. Since there is no outside force to apply motion to the pendulum, the arc of the movement from point 1 to point 3 will decrease. This is when volatility declines. Some call this complacency, but it is generally viewed as a market with low or declining volatility.
In the chart below, observe the relative volatilities and the deviations thereof over the course of the recent market meltdown. Click here for a larger view of the historical volatility chart. Volatility and Options Volatility is one of the many important inputs -- along with market price, strike price, interest rates, dividends and time -- in calculating the value of an option. The most popular options pricing model is Black-Scholes. If you desire to torture yourself with how the Black-Scholes options pricing model works, I have provided a link for further reference.
When calculating an option price, one merely inputs the volatility as a given for the reference security underlying security, in options speak for a period of time to match the remaining days to expiration, along with the other required variables, into the Black-Scholes model, and out pops the option valuation.
To learn more about options, check out the Futures and Options section of TheStreet University's Getting Started index. Implied Volatility The options market is a bid and offer system in which buyers and sellers come together in an auction environment to actuate price discovery and execute trades.
These prices are quoted in dollars and cents.
From these prices, knowing all of the other Black-Scholes variables and using the Black-Scholes formula, we can calculate the volatility, which is implicit from a traded price or the bid and offer. This is referred to as the option's implied volatility. Whereas historic volatility is static for a fixed given period of time, please note that implied volatility will vary for a stock based on different options strike prices. This is referred to as the volatility skew.
How to Calculate Annualized Volatility -- The Motley Fool
As was the case with historical volatility, the weighted implied volatilities were higher for RACK and lower for JNJ. However, the impact of the market correction was felt more by JNJ than RACK because of the already elevated implied volatility for RACK. Also, observe that the implied volatilities for both JNJ and RACK are higher than the historical volatilities. This is due to the speculative nature of options trading. Click here for a larger view of the implied volatility chart.
This concept is taken one step further. For many indices, a volatility index has been created and is commonly quoted in the financial media. The three most common ones: Many market participants and observers will use these indices as a gauge of market sentiment. The CBOE Web site has some interesting information on the VIX, other volatility indices and related products. Presented below are the volatility indices for March 6, and the week prior to that date after the market took its big one-day plunge.
Note the huge surge in volatility in response to the market drop.
Also, observe the relationship between the individual stocks' implied volatilities and that of the indices. RACK options, on the other hand, are significantly more volatile in implied measures than options for the tech-heavy Nasdaq Volatility Index.
Click here to view the volatility indices chart.
Measuring Stock Market Volatility - The Daily Reckoning
Intraday Volatility Finally, we have intraday volatility. This represents the market swings during the course of a trading day and is the most noticeable and readily available definition of volatility. Intraday volatility is the Justice Potter Stewart type of volatility because it's hard to define but you know it when you see it. A common mistake is equating intraday volatility with the implied volatility index. Both of these forms of volatility are not interchangeable, but do carry their own importance in ascertaining investor sentiment and expectations.
The first is intraday volatility which reflects the difference between the high and low on the day divided by the closing price of the day for the SPX. The second, LakeView Asset Management VDEV, is a proprietary measure of volatility that I created using historical trends in the SPX to predict future volatility.
The VDEV will be discussed in a future installment of this series. Click here for a larger view the intraday volatility chart. In summary, here is a recap of the four types of volatility: Action Alerts PLUS is a registered trademark of TheStreet, Inc.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience. Jim Cramer's Best Stocks for Most Recent Trade Alert. Subscribe Access insights and guidance from our Wall Street pros. Find the product that's right for you. Mar 12, Prev 0 of 4 Next. Jul 20, Jul 11, 7: Jun 27, 7: Jun 22, 7: Advanced Micro Devices Stock Explodes After Releasing Details on New Super Chip, Epyc. Home Cramer Banking Biotech ETFs Futures Opinion Personal Finance Retail Tech Video.
Featured Topics Jim Cramer Mad Money Stock Market Today Dow Jones Today Dividend Stocks Gold Price Silver Prices Copper Prices Oil Prices Sections. Popular Pages Best Stocks Best Stocks to Buy High Dividend Stocks Stock Market Holidays Earnings Calendar Ex Dividend Date ETF Ratings Mutual Fund Ratings Best Online Brokers.
Stay Connected Feedback About Us Investor Relations Advertise Reprints Customer Service Employment Privacy Policy Terms of Use Topic Archive Video Sitemap Data Affiliate Press Room.